Here I am going to provide you CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce Notes. By going through Reproduction Class 10 Notes you can revise the How Do Organisms Reproduce chapter in a very effective way. I hope that this will certainly help you in your studies!
Introduction
- Reproduction is the process by which living organisms produce new individuals similar to themselves. It ensures continuity of life on earth.
- Reproducing organisms create new individuals that look very much like themselves.
- If there were to be only one, non-reproducing member of a particular kind, it is doubtful that we would've noticed its existence.
Do Organisms Create Exact Copies of Themselves?
- Organisms look similar because their body designs are similar.
- If body designs are to be similar, the blueprints for these designs should be similar.
- Thus, reproduction at its most basic level will involve making copies of the blueprints of body design.
- Therefore, a basic event in reproduction is the creation of a DNA copy. Cells use chemical reactions to build copies of their DNA.
Asexual Reproduction
- A single individual give rise to new individual.
- Gametes are not formed.
- New individual is identical to parent.
- It is extremely useful as a means of rapid multiplication.
- Adopted by lower organisms.
Modes of Asexual Reproduction
Fission
- The parent cell divides into daughter cells.
- Many bacteria and protozoa simply split into two equal halves during cell division.
Many different patterns of fission have been observed.
- Binary fission: 2 cells are formed. Example: amoeba.
- Multiple fission: Many cells are formed. Example: Plasmodium
Fragmentation
- The organism breaks-up into smaller pieces upon maturation, each piece develops into new individual.
- Example: Spirogyra.
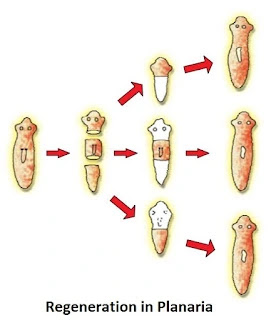
Regeneration
- If organism is somehow cut or broken into many pieces, each piece grows into a complete organism.
- Example: Planaria, Hydra.
Budding
- A bud is formed which develops into tiny individual. It detaches from parent body upon maturation and develops into new individual.
- Example: Hydra
Vegetative Propagation
In many plants, new plants develops from vegetative parts such as:
- By roots: Example: dahlias, sweet potato.
- By stem: Example: potato, ginger.
- By leaves: Example: bryophyllum (leaf notches bear buds which develop into plants).
Artificial methods in Vegetative Propagation
- Grafting: Example: Mango
- Cutting: Example: Rose
- Layering: Example: Jasmine
- Tissue culture: New plants are grown by using growing tip of a plant. These growing cells are kept in a culture medium leads to the formation of callus. Callus is then transferred to hormone medium which causes growth and differentiation. Example: ornamental plants, orchid.
- Benefits of tissue culture
- We can grow plants like banana, rose, jasmine etc. that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
- New plants are genetically similar to parents.
- Helps in growing seedless fruits.
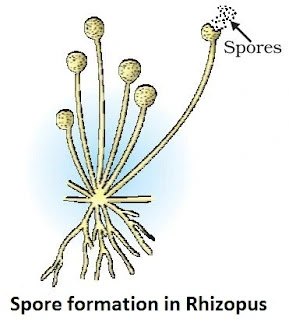
Spore Formation
Spores are small bulb like structures which are covered by thick walls. Under favourable conditions, they germinate and produce new organism.
Example: Rhizopus
Sexual Reproduction
- Two individuals i.e., one male and one female are needed to give rise to new individual.
- Gametes are formed.
- New individual is genetically similar but not identical to parents.
- It is useful to generate more variations in species.
- Adopted by higher organisms.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
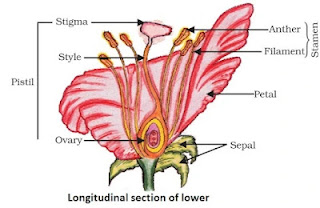
- Flowers are the reproductive organs of plants.
- A typical flower consists of four main whorls namely sepals, petals, stamen and pistil.
Types of Flowers
- Bisexual flower: Both male and female reproductive parts are present. Example: Hibiscus, mustard.
- Unisexual flower: Either male or female reproductive part is present. Example: Papaya, watermelon.
Process of Seed Formation
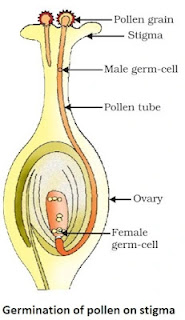
- Pollen grains, produced in the anther, are transferred to the stigma of same flower (self pollination) or stigma of another flower (cross pollination) through agents like air, water or animals.
- Pollen grains germinate and form pollen tubes which pass through style to reach upto the ovules present in ovary.
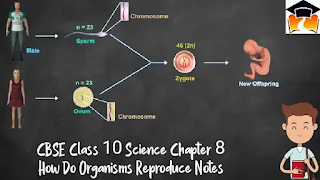
- The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilization. Zygote is produced inside the ovary.
- Zygote divides to form embryo. Ovule develops thick coat and changes into seed gradually.
- Ovary changes into fruit and other parts of flower fall off.
- The seed germinates to form a plant under suitable conditions such as air, moisture etc.
Reproduction in Human Beings
- Humans use sexual mode of reproduction.
- Sexual maturation: The period of life when production of germ cells i.e. ova (female) and sperm (male) start in the body. This period of sexual maturation is called puberty.
Changes at Puberty
- Thick hair growth in armpits and genital area.
- Skin becomes oily, may result in pimples.
- Breast size begin to increase.
- Girls begin to menstruate.
- Thick hair growth on face.
- Voice begin to crack.
Male Reproductive System
Testes
- A pair of testes are located inside scrotum which is present outside the abdominal cavity.
- Scrotum has a relatively lower temperature needed for the production of sperms.
- Male germ cell i.e. sperms are formed here.
- Testes release male sex hormone (testosterone).
- Regulate production of sperms.
- Bring changes at puberty.
Vas deferens
- It passes sperms from testes upto urethera.
Urethera
- It is a common passage for both sperms and urine. Its outer covering is called penis.
Associated glands
- Seminal vesicles and prostate gland add their secretion to the sperms. This fluid provide nourishment to sperms and make their transport easy.
- Sperm along with secretion of glands form semen.
Female Reproductive System
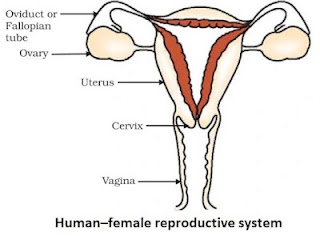
Ovary
- A pair of ovary is located in both sides of abdomen.
- Female germ cells i.e. eggs are produced here.
- At the time of birth of a girl, thousands of immature eggs are present in the ovary.
- At the onset of puberty, some of these eggs start maturing.
- One egg is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
Oviduct or Fallopian tube
- Receives the egg produced by the ovary and transfer it to the uterus.
- Fertilisation i.e. fusion of gametes takes place here.
Uterus
- It is a bag-like structure where development of the baby takes place.
- Uterus opens into vagina through cervix.
Fertilisation of egg
When egg is fertilised
- The fertilized egg called zygote is planted in uterus and develops into an embryo.
- The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. It provides a large surface area for the exchange of glucose, oxygen and waste material.
- The time period from fertilization upto the birth of the baby is called gestation period. It is about 9 months.
When egg is not fertilised
- The uterus prepares itself every month to receive fertilized egg.
- The lining of the uterus becomes thick and spongy, required to support the embryo.
- When fertilisation had not taken place, this lining is not needed any longer.
- This lining breaks and comes out through vagina as blood and mucus.
- This cycle takes around 28 days every month and called menstruation.
Reproductive Health
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
- Bacterial : Gonorrhoea and syphilis
- Viral : Warts and HIV-AIDS
Contraception
It is the avoidance of pregnancy, can be achieved by preventing the fertilisation of ova.
Methods of contraception
Physical barrier
- To prevent union of egg and sperm.
- Use of condoms, cervical caps and diaphragm.
- Use of oral pills
- These change hormonal balance of body so that eggs are not released.
- May have side effects.
- Copper-T or loop is placed in uterus to prevent pregnancy.
- In males the vas deferens is blocked to prevent sperm transfer called vasectomy.
- In females, the fallopian tube is blocked to prevent egg transfer called tubectomy.
Female Foeticide
- The practice of killing a female child inside the womb is called female foeticide.
- For a healthy society, a balanced sex ratio is needed that can be achieved by educating people to avoid malpractices like female foeticide and prenatal sex determination.
- Prenatal sex determination is a legal offence in our country so as to maintain a balanced sex ratio.
More resources for class 10:
Chapterwise NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapterwise Notes
Chapterwise NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Social Science
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapterwise Notes
Chapterwise NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Sanskrit
CBSE Class 10 Sanskrit Chapterwise Summary